This profile has been superseded by the 2019 version, which is available here.
View the complete Australian forest profiles series.
Information for this profile is drawn from Australia's State of the Forests Report 2013.
 Australia has 1.3 million hectares of the Casuarina forest type, including forests dominated by species of Casuarina (six species) or Allocasuarina (59 species). Casuarinas are commonly called she-oaks because of the similarity of their timber to that of European oaks. They are a distinctive part of many Australian coastal and riverine landscapes.
Australia has 1.3 million hectares of the Casuarina forest type, including forests dominated by species of Casuarina (six species) or Allocasuarina (59 species). Casuarinas are commonly called she-oaks because of the similarity of their timber to that of European oaks. They are a distinctive part of many Australian coastal and riverine landscapes.
Casuarina foliage typically comprises numerous slender, wire-like jointed branchlets that droop from the tree’s branches.
Distribution and ownership
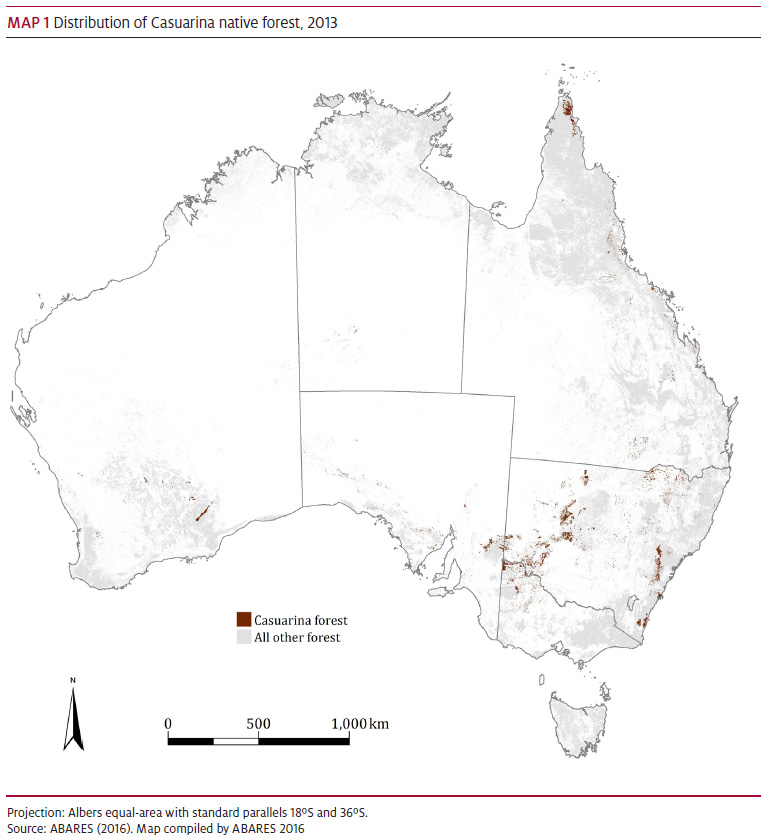
Casuarina forests are found in all of Australia’s states and territories (Map 1). A total of 0.6 million hectares (44 per cent) of the Casuarina forest type is in New South Wales and 0.3 million hectares (23 per cent) are in Queensland.
Open a high-resolution version of Map 1 that can be saved as a PNG file
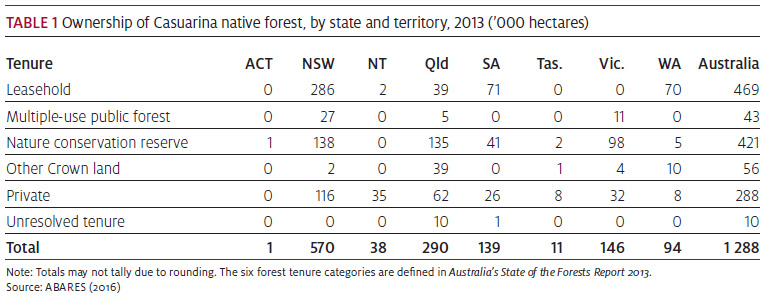
A total of 0.5 million hectares (37 per cent) of Casuarina forest is on leasehold land and 0.4 million hectares (33 per cent) are on nature conservation reserves (Table 1). Large areas are found in national parks, including the Murray-Sunset National Park in western Victoria and the Wadbilliga National Park in south-eastern New South Wales.
Download Table 1 data as an Excel workbook
Forest structure
Only some species of casuarina form forest communities; others grow in vegetation too short or sparse to be classified as forest. The tallest casuarina trees grow along rivers, where individual trees can grow to more than 20 metres tall. Common inland species include belah (C. cristata), desert oak (A. decaisneana) and river she-oak (C. cunninghamiana).
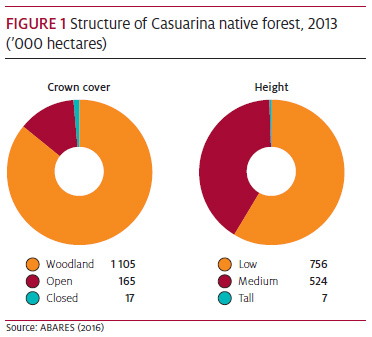
Eighty-five per cent (1.1 million hectares) of Casuarina forest is woodland forest and 59 per cent (0.8 million hectares) is low forest (Figure 1).

Importance and uses
Casuarinas can fix nitrogen, which is an essential nutrient for plant growth. This process depends on symbiotic bacteria that live in the plant’s root system. Nitrogen fixation provides an additional nitrogen source for wider forest ecosystems.
Some species of casuarina, such as river she-oak, grow along river and stream banks. Their roots help stabilise the banks, which reduces surface-water runoff, erosion and sedimentation. This helps maintain water quality for environmental and recreational purposes.
Casuarina wood is dense and very hard, which makes it an excellent fuelwood. Indigenous Australians have traditionally used the wood for shields, clubs and boomerangs. In colonial times, wood from various species was used for roof shingles, fencing, handles and bullock yokes.
Timber from some casuarinas has an attractive wide, dark-coloured grain and is used for wood-turning, small cabinetwork and parquetry.
Bibliography
ABARES 2016, Forests of Australia (2013) v2.0, Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences.
Boland, D, Brooker, M, Chippendale, G, Hall, N, Hyland, B, Johnston, R, Kleinig, D, McDonald, M & Turner, J 2006, Forest trees of Australia, 5th edn, CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne.
Carnahan, JA 1990, Atlas of Australian resources, vol. 6, Vegetation, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra.
Montreal Process Implementation Group for Australia & National Forest Inventory Steering Committee 2013, Australia’s State of the Forests Report 2013, Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences, Canberra.
