Australia’s forests and forestry glossary
Water quality
A property of water derived from the level of nutrients, particles and chemicals contained in water. Low levels of these components are associated with high water quality.
Water yield
The amount of water that flows out of a catchment (drainage basin).
See Catchment.
Watercourse
A natural or artificial water drainage channel. A watercourse may carry surface water flows intermittently or permanently.
Watershed
The dividing line between two catchments (drainage basins).
See Catchment.
Watertable
The underground level at which the ground is saturated with water, where the water pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure.
Wet forest/wet sclerophyll forest
Typically, eucalypt-dominated sclerophyll forest (not dry forest or rainforest) associated with moist (mesic) conditions, and with an understorey (if present) dominated or co-dominated by rainforest species or non-sclerophyll shrubs.
See Dry forest/dry sclerophyll forest, Eucalypt, Rainforest, Sclerophyll, Understorey.
Wetland
Areas of swamp, marsh, fen, peatland or mangrove, whether natural or artificial, and permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, and fresh, brackish or salt.
Forest wetlands are wetland ecosystems where forests are present.
See Mangrove.
Wild harvest
Commodity or product harvested from the wild, including farming of wildlife and feral animals.
Wilderness
Land that, together with its plant and animal communities, has not been substantially modified by, and is remote from, the influences of European settlement, or is capable of being restored to such a state; is of sufficient size to make its maintenance in such a state feasible; and can provide opportunities for solitude and self-reliant recreation.
Wildfire
See Bushfire.
Wildlife corridor
An area or strip of suitable habitat connecting wildlife populations otherwise separated by human activities.
See Connectivity, Fragmentation.
Wildling
A plant of a plantation tree species that has grown independently in forest or land adjoining the plantation.
Windthrow
Trees uprooted or broken as a result of severe wind associated with storms; the process of uprooting or breaking trees in this way.
See Disturbance.
Wood
The hard, fibrous, underbark component of the stem and/or branches of a tree, often suitable for conversion into products.
Woodchips
Small chips of wood produced from logs for use in fibre products or for conversion to pulp for paper manufacture.
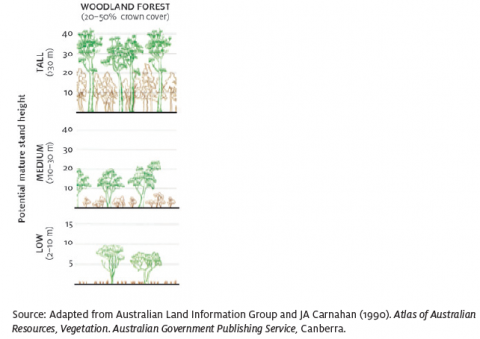
Woodland forest
As a National Forest Inventory cover class, native forest in which the tree crowns cover between 20% and 50% of the land area.
See Closed forest, Crown cover, National Forest Inventory, Open forest, Sparse woody vegetation.
Click here for an enlarged version.
World Heritage
Areas deemed to have outstanding universal value for humankind under an international convention (the World Heritage Convention) to which Australia is a signatory.
