Key issues
- During the week ending 25 August 2021, high pressure systems and weak frontal activity across southern Australia resulted in little rainfall across much of the continent. Weak frontal systems brought rainfall to western Tasmania, parts of southern Victoria and the southwest of Western Australia. An east coast low-pressure system produced isolated heavy rainfall in south-eastern Australia.
- The dry conditions across most of Australia’s cropping regions would have allowed growers to access fields to apply urea and spray for pests and diseases. Most cropping regions would benefit from some rainfall in the coming weeks to maintain the current high yield prospects in many regions.
- A negative Indian Ocean Dipole event has persisted throughout August and is expected to continue into spring. The event was officially declared by the Bureau of Meteorology last month, following eight weeks of negative index values. The Southern Annular Mode has rapidly shifted from negative to positive values over the past week and is likely to influence the Australian climate over the coming week.
- The outlook for September 2021 indicates that there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 10 and 100 millimetres across parts of eastern, south-western and far southern Australia. Rainfall totals in excess of 100 millimetres are expected across isolated parts of Victoria and the west coast of Tasmania.
- The outlook for September to November suggests there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 50 and 200 millimetres across much of New South Wales and Victoria, eastern Queensland, the south of South Australia, the south of Western Australia, large parts of the Northern Territory and eastern Tasmania. Rainfall totals in excess of 300 millimetres are likely across parts of alpine and coastal regions of New South Wales and Victoria and western Tasmania.
- High pressure systems are likely to bring clear skies and dry conditions across much of Australia over the next eight days. Parts of southern Australia are expected to receive rainfall from cold fronts moving off the Southern Ocean, and moist onshore flow is likely to bring rainfall to tropical north Queensland. The dry conditions across most cropping regions are expected to allow for continued unimpeded access for crop management activities. Most regions have average to above-average soil moisture levels, which will support ongoing crop development.
- Water storage in the Murray–Darling Basin (MDB) increased by 224 gigalitres (GL) between 17 August 2021 and 25 August 2021. The current volume of water held in storage is 20,119 GL, which represents 79% of total capacity. This is 46% or 6,300 GL more than at the same time last year
- Allocation prices in the Victorian Murray below the Barmah Choke increased from $117 per ML on 13 August 2021 to $124 per ML on 20 August 2021. Prices are lower in the Goulburn-Broken, Murrumbidgee, and regions above the Barmah choke due to the binding of the Goulburn intervalley trade limit, Murrumbidgee export limit, and Barmah choke trade constraint.
Climate
[expand all]
Rainfall this week
During the week ending 25 August 2021, high pressure systems and weak frontal activity across southern Australia resulted in little rainfall across much of the continent. Weak frontal systems brought rainfall to western Tasmania, parts of southern Victoria and the southwest of Western Australia. An east coast low-pressure system produced isolated heavy rainfall in south-eastern Australia.
Rainfall totals of between 10 and 50 millimetres were recorded across much of eastern New South Wales, southern and eastern Victoria, the far southwest of Western Australia, much of Tasmania and isolated areas of Queensland. Rainfall totals in excess of 50 millimetres were recorded across parts of eastern New South Wales and Victoria, and western Tasmania.
In cropping regions, rainfall totals of between 15 and 50 millimetres were recorded across most of central and northern New South Wales. Lower weekly rainfall totals of between 5 and 15 millimetres were recorded across the remainder of New South Wales and parts of southern Queensland and South Australia. Little to no rainfall was recorded in remaining cropping regions in Queensland and South Australia as well as most cropping regions in Victoria and Western Australia.
The dry conditions across most of Australia’s cropping regions would have allowed growers to access fields to apply urea and spray for pests and diseases. Most cropping regions would benefit from some rainfall in the coming weeks to maintain the current high yield prospects in many regions.
Rainfall for the week ending 25 August 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 25/08/2021
Note: The rainfall analyses and associated maps utilise data contained in the Bureau of Meteorology climate database, the Australian Data Archive for Meteorology (ADAM). The analyses are initially produced automatically from real-time data with limited quality control. They are intended to provide a general overview of rainfall across Australia as quickly as possible after the observations are received. For further information go to http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/rainfall/
Climate Drivers
Throughout winter the climate drivers with the largest potential impact on Australia’s climate patterns are the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and the Southern Annular Mode (SAM). These climate drivers will likely influence the outlook for Australia’s winter cropping season.
A negative IOD event has persisted throughout August and is expected to continue into Spring. The event was officially declared by the Bureau of Meteorology last month, following eight weeks of negative index values. The SAM has rapidly shifted from negative to positive values over the past week and is likely to influence the Australian climate over the coming week. A positive SAM typically brings decreased rainfall for much of Victoria, the west of Western Australia and Tasmania.
Oceanic and atmospheric indicators show ENSO conditions remain neutral, reducing its influence on Australia’s climate. International climate models surveyed by the Bureau of Meteorology agree that ENSO conditions are likely to remain neutral throughout September. Three of the seven models, however, expect the development of a La Niña event in late spring. Only one model expects a La Niña event in December.
Sea surface temperature anomalies have been close to average across the tropical Pacific Ocean over the previous week. Warm anomalies in the western Pacific have strengthen slightly, while warm anomalies near the Maritime Continent and along the east coast of Australia have remained largely unchanged. Neutral Pacific equatorial sea surface temperatures are associated with neutral ENSO conditions.
Warm sea surface temperature anomalies have weakened slightly near Western Australia and Indonesia. Meanwhile, sea surface temperatures in the western Indian Ocean largely remained neutral over the past week. The continuation of warm anomalies in the eastern Indian Ocean and the ocean surrounding Australia reflect the ongoing negative IOD event.
Difference from average sea surface temperature observations 9 August to 15 August 2021
As at 15 August, the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) weekly value was -0.37°C, although it has largely remained below the negative threshold (-0.4°C). A negative IOD event increases the chance of above average rainfall for southern and eastern Australia and the far north during winter and spring and is typically associated with an early onset of northern rainfall. It also increases the chances of below average maximum temperatures in southern Australia, while increasing the chances of above average minimum and maximum temperatures in northern Australia.
Monthly sea surface temperature anomalies for IOD region
The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) is currently positive. The SAM refers to the north-south shift of the band of rain-bearing westerly winds and weather systems in the Southern Ocean compared to the usual position. When SAM is positive during winter, the band of westerly winds is further south than normal. A negative SAM in winter is associated with increased rainfall for northern New South Wales, southern Queensland and southern parts of South Australia and Western Australia. It is also associated with decreased rainfall for much of Victoria, the west of Western Australia and Tasmania.
Southern Annular Mode (SAM) daily index
National Climate Outlook
These climate outlooks are generated by ACCESS–S (Australian Community Climate Earth-System Simulator–Seasonal). ACCESS–S is the Bureau of Meteorology's dynamical (physics-based) weather and climate model used for monthly, seasonal and longer-lead climate outlooks.
For further information, go to http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/ahead/about/
The Bureau of Meteorology’s latest rainfall outlook indicated wetter than average conditions are expected for much of Australia during September. The wetter than average conditions expected for most cropping regions reaffirms the positive production outlook for Australia’s 2021 winter cropping season. The ACCESS-S climate model suggests there is close to a 60% chance of exceeding average September rainfall totals across much of Australia.
The outlook for September 2021 indicates that there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 10 and 100 millimetres across parts of eastern, south-western and far southern Australia. Rainfall totals in excess of 100 millimetres are expected across isolated parts of Victoria and the west coast of Tasmania.
Across cropping regions there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals of between 5 and 10 millimetres in parts of northern and south-western Queensland. There is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 10 and 50 millimetres for New South Wales, south-east Queensland, Victoria, South Australia and much of Western Australia.
The expected rainfall will add to the average to above average soil moisture levels across most cropping regions. Entering spring, high levels of plant available water will support crops through flowering and grain filling, providing a positive outlook for yield potentials.
Rainfall totals that have a 75% chance of occurring September 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 19/08/2021
The rainfall outlook for September to November suggests there is a greater than 75% chance of exceeding average rainfall across much of New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, South Australia and the Northern Territory. There is no strong tendency toward above or average rainfall across the much of Western Australia and parts of Tasmania (Bureau of Meteorology ‘National Climate Outlook’, 19 August 2021).
Bureau of Meteorology rainfall outlooks for September to November have greater than 55% past accuracy across most of Australia. Outlook accuracy is greater than 65% New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia and Tasmania, as well as much of Victoria and the Northern Territory. On the other hand, there is low past accuracy in western and central Western Australia and isolated areas of south-eastern New South Wales and Victoria.
Chance of exceeding the median rainfall September to November 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 19/08/2021
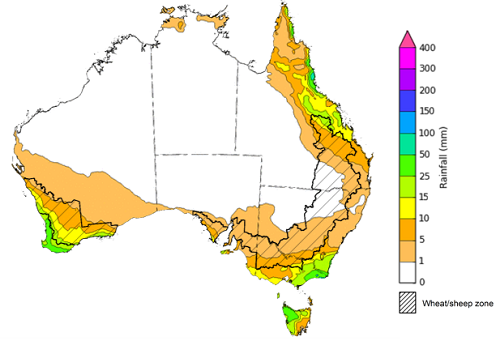
The outlook for September to November suggests there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 50 and 200 millimetres across much of New South Wales and Victoria, eastern Queensland, the south of South Australia, the south of Western Australia, large parts of the Northern Territory and eastern Tasmania. Rainfall totals in excess of 300 millimetres are likely across parts of alpine and coastal regions of New South Wales and Victoria and western Tasmania.
Across cropping regions, there is a 75% chance of receiving between 50 and 200 millimetres in New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, South Australia and southern parts of Western Australia. Totals of less than 50 millimetres are expected across much of the northern cropping areas of Western Australia.
These rainfall totals are slightly below average for this three-month period across some Western Australian cropping regions, and slightly above average for cropping regions of New South Wales, Queensland and Victoria. Average to above average soil moisture levels across most cropping regions, and the probability of close to average in-season rainfall in September to November, will assist crops through critical development stages and improve yield potentials for winter crops and allow for the planting of summer crops in spring.
Rainfall totals that have a 75% chance of occurring September to November 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 19/08/2021
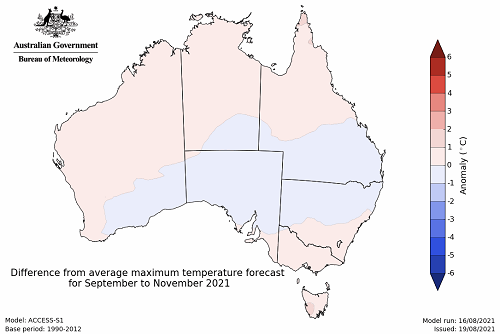
The temperature outlook for September to November 2021 indicates that maximum temperatures across most of Australia are likely to be close to the 1990-2012 average (- 1°C to 1°C). Minimum temperatures are expected to be slightly above average for much of Queensland and the Northern Territory, as well as parts of New South Wales, South Australia and Western Australia (Bureau of Meteorology ‘National Climate Outlook’, 19 August 2021).
Predicted maximum temperature anomaly for September to November 2021
Predicted minimum temperature anomaly for September to November 2021
Rainfall forecast for the next eight days
High pressure systems are likely to bring clear skies and dry conditions across much of Australia over the next eight days. Parts of southern Australia are expected to receive rainfall from cold fronts moving off the Southern Ocean, and moist onshore flow is likely to bring rainfall to tropical north Queensland.
Rainfall totals of between 10 and 50 millimetres are forecast for parts of far south-east New South Wales, southern and eastern Victoria, north-east Queensland, the south-west of Western Australia and eastern Tasmania. Rainfall in excess of 50 millimetres is expected in north-eastern Queensland, parts of south-west Western Australia and western Tasmania.
In Australian cropping regions, rainfall totals of between 5 and 15 millimetres are expected in parts of southern Victoria, northern Queensland and much of Western Australia. Little to no rainfall is forecast for much of New South Wales, remaining areas in Queensland, northern Victoria and much of South Australia during the next 8-days.
The dry conditions across most cropping regions are expected to allow for continued unimpeded access for crop management activities. Most regions have average to above-average soil moisture levels, which will support ongoing crop development. If the expected falls across Western Australia eventuate as forecast, they will support the current high yield prospects in that state.
Total forecast rainfall (mm) for the period 26 August to 2 September 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 26/08/2021
Water
Water storages, water markets and water allocations - current week
The Tableau dashboard may not meet accessibility requirements. For information about the contents of these dashboards contact ABARES.
Commodities
Information on weekly price changes in agricultural commodities is now available at the Weekly commodity price update.
Key issues
- During the week ending 11 August 2021, low pressure systems and cold fronts brought rainfall to parts of western and southern Australia. High pressure systems and clear skies, on the other hand, resulted in little to no rainfall across much of eastern, central and northern Australia.
- For the 3 months to July 2021, low rainfall totals limited pasture production across parts of southern and northern Australia. In contrast, average or better rainfall and generally average soil moisture benefitted pasture production across large areas of western and eastern Australia.
- The Bureau of Meteorology reports that the negative Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) event continues. A negative IOD event increases the chance of above average rainfall for southern and eastern Australia and the far north during winter and spring. It is also typically associated with an early onset of northern rainfall.
- The outlook for September 2021 indicates that there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 10 and 100 millimetres across parts of eastern, south-western and far southern Australia. Rainfall totals in excess of 100 millimetres are expected across alpine regions of New South Wales and Victoria, and western Tasmania.
- The rainfall outlook for spring 2021 (September to November) suggests there is a greater than 70% chance of exceeding average rainfall across much of New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, South Australia and the Northern Territory. There is an increased chance of below average rainfall across the north and part of south-west Western Australia and western Tasmania during spring 2021.
- The influence of slow-moving high-pressure systems is likely to bring clear skies and dry conditions across much of Australia over the next eight days. Rainfall is likely to be limited to west facing southern coastlines and onshore flow will bring showers to isolated areas of Australia’s eastern coast.
- Little to no rainfall is forecast for most of Australia’s cropping regions during the next 8-days. These dry conditions across most cropping regions will allow for drying of saturated soil profiles in some areas, reducing the impact of waterlogging and associated water-damage. Crop development is expected to progress unimpeded with high levels of plant available moisture in most areas provided by previous heavy falls.
- Water storage in the Murray–Darling Basin (MDB) increased by 317 gigalitres (GL) between 4 August 2021 and 11 August 2021. The current volume of water held in storage is 19,638 GL, which represents 78% of total capacity. This is 54% or 6,889 GL more than at the same time last year.
- Allocation prices in the Victorian Murray below the Barmah Choke decreased from $125 per ML on 30 July 2021 to $113 per ML on 6 August 2021. Prices are lower in the Goulburn-Broken, Murrumbidgee, and regions above the Barmah choke due to the binding of the Goulburn intervalley trade limit, Murrumbidgee export limit, and Barmah choke trade constraint.
Climate
[expand all]
Rainfall this week
During the week ending 11 August 2021, low pressure systems and cold fronts brought rainfall to parts of western and southern Australia. High pressure systems and clear skies, on the other hand, resulted in little to no rainfall across much of eastern, central and northern Australia.
Rainfall totals of between 10 and 50 millimetres were recorded across isolated parts of Queensland, Victoria, southern South Australia, much of the south-west of Western Australia and western Tasmania. Rainfall totals in excess of 50 millimetres were recorded in isolated parts of south-west Western Australia and western Tasmania.
In cropping regions, rainfall totals of between 10 and 50 millimetres were recorded across much of Western Australia. Little to no rainfall was recorded in cropping regions of New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria and South Australia.
Continued wet conditions in the south-west of Western Australia has likely exacerbated waterlogging in some areas, negatively impacting crop growth. The drier conditions in eastern cropping regions provided a welcome break, with ample soil moisture to support ongoing plant development. Recent wet conditions across Australia have restricted access to fields and delayed spraying of crops for pest and disease control and applications of urea. A run of dry weather in some eastern and western cropping regions will be required to allow field access, otherwise aerial spraying may become necessary.
Rainfall for the week ending 11 August 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 11/08/2021
Note: The rainfall analyses and associated maps utilise data contained in the Bureau of Meteorology climate database, the Australian Data Archive for Meteorology (ADAM). The analyses are initially produced automatically from real-time data with limited quality control. They are intended to provide a general overview of rainfall across Australia as quickly as possible after the observations are received. For further information go to http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/rainfall/
Pasture Growth
Pasture growth during the May to July period is typically low across large areas of central and northern Australia as it enters a seasonally low growth period due to cooler temperatures and little to no rainfall. Across southern Australia, May to July pasture growth influences the number of livestock than can be supported without supplementary feeding over winter and the level of reliance on hay and grain during this period.
For the 3 months to July 2021, low rainfall totals limited pasture production across parts of southern and northern Australia. In contrast, average or better rainfall and generally average soil moisture benefitted pasture production across large areas of western and eastern Australia.
Modelled pasture growth was extremely low to below average across parts of western New South Wales, parts of central Queensland, western Victoria, eastern South Australia, central and northern Western Australia, and parts of central Northern Territory. As a result, livestock producers across parts of western New South Wales, western Victoria and eastern South Australia will be heavily reliant on rainfall over the remainder of winter to build soil moisture levels and supplementary feed to maintain current stock numbers.
In contrast, modelled pasture growth was above average to extremely high across large areas of central and northern New South Wales, eastern Queensland, and large areas of Western Australia. This growth is likely to enable farmers to continue to rebuild stock numbers and provide opportunities to replenish fodder supplies during spring.
Relative pasture growth for 3-months ending July 2021 (1 May to 31 July 2021)
Notes: AussieGRASS pasture growth estimates are relative to the long-term record and shown in percentiles. Percentiles rank data on a scale of zero to 100. This analysis ranks pasture growth for the selected period against average pasture growth for the long-term record (1957 to 2016). Pasture growth is modelled at 5km2 grid cells.
Source: Queensland Department of Science, Information Technology and Innovation
Climate Drivers
Throughout winter the climate drivers with the largest potential impact on Australia’s climate patterns are the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and the Southern Annular Mode (SAM). These climate drivers will likely influence the outlook for Australia’s winter cropping season.
The Bureau of Meteorology reports that the negative Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) event continues. A negative IOD event increases the chance of above average rainfall for southern and eastern Australia and the far north during winter and spring. It is also typically associated with an early onset of northern rainfall.
ENSO conditions, on the other hand, remain neutral according to most oceanic and atmospheric indicators, reducing its influence on Australia’s climate. International climate models surveyed by the Bureau of Meteorology agree that ENSO conditions are likely to remain neutral throughout August. Three of the seven models, however, expect the development of a La Niña event in mid-to-late spring. Only two models expect a La Niña event in December. The SAM is currently positive but is expected to rapidly return to neutral values over the coming days and remain there in the coming weeks. It is therefore unlikely to have a significant influence on Australia’s climate.
Sea surface temperature anomalies were close to average across the tropical Pacific Ocean over the previous week. Warm anomalies in the western Pacific have weakened slightly, while warm anomalies near the Maritime Continent and along the east coast of Australia have persisted. Neutral Pacific equatorial sea surface temperatures are associated with neutral ENSO conditions.
Warm sea surface temperature anomalies have persisted near Western Australia and Indonesia. Meanwhile, sea surface temperatures in the western Indian Ocean largely cooled slightly over the past week. The warm anomalies in the eastern Indian Ocean and the ocean surrounding Australia underpin the continuation of the negative IOD event.
Difference from average sea surface temperature observations 26 July to 1 August 2021
As at 1 August 2021, the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) weekly value was -0.76°C. The IOD index has generally been below the negative IOD threshold (−0.4 °C) since mid-May. A negative IOD, and warmer sea surface temperatures in the eastern Indian Ocean, is associated with above average rainfall for much of southern Australia in winter and spring. It also increases the chances of below average maximum temperatures in southern Australia, while increasing the chances of above average minimum and maximum temperatures in northern Australia.
The majority of international climate models surveyed by the Bureau of Meteorology expect the negative IOD event to persist until November, with all but one model expecting a return to neutral conditions in December.
Monthly sea surface temperature anomalies for IOD region
National Climate Outlook
These climate outlooks are generated by ACCESS–S (Australian Community Climate Earth-System Simulator–Seasonal). ACCESS–S is the Bureau of Meteorology's dynamical (physics-based) weather and climate model used for monthly, seasonal and longer-lead climate outlooks.
For further information, go to http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/ahead/about/
The Bureau of Meteorology’s latest rainfall outlook indicated wetter than average conditions are expected for much of eastern and central Australia during August. The wetter than average conditions expected for most cropping regions reaffirms the positive production outlook for Australia’s 2021 winter cropping season. The ACCESS-S climate model suggests there is close to a 65% chance of exceeding average September rainfall totals across much of Australia.
The outlook for September 2021 indicates that there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 10 and 100 millimetres across parts of eastern, south-western and far southern Australia. Rainfall totals in excess of 100 millimetres are expected across alpine regions of New South Wales and Victoria, and western Tasmania.
Across cropping regions there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals of between 5 and 10 millimetres in parts of northern Queensland. There is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 10 and 50 millimetres for New South Wales, southern Queensland, Victoria, South Australia and Western Australia. This expected rainfall for September is likely to be sufficient to support the ongoing growth, and eventual yield development, of winter crops in most regions.
Rainfall totals that have a 75% chance of occurring September 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 05/08/2021
The rainfall outlook for spring 2021 (September to November) suggests there is a greater than 70% chance of exceeding average rainfall across much of New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, South Australia and the Northern Territory. There is an increased chance of below average rainfall across the north and part of south-west Western Australia and western Tasmania during spring 2021 (Bureau of Meteorology ‘National Climate Outlook’, 5 August 2021).
Bureau of Meteorology rainfall outlooks for spring have greater than 55% past accuracy across most of Australia. Outlook accuracy is greater than 65% across much of New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia and much of the Northern Territory. On the other hand, there is low past accuracy for large areas of northern and central Western Australia.
Chance of exceeding the median rainfall September to November 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 05/08/2021
The outlook for spring 2021 suggests there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 50 and 200 millimetres across much of New South Wales, Victoria, southern and eastern Queensland, the south of Southern Australia, the far south-west and north-east of Western Australia, Tasmania, and large areas of the Northern Territory. Rainfall totals in excess of 300 millimetres are likely across parts of eastern New South Wales and Victoria, and western Tasmania.
Across cropping regions, there is a 75% chance of receiving between 50 and 200 millimetres in New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Queensland and southern Western Australia. Totals of less than 50 millimetres are expected across remaining cropping regions in Western Australia.
These rainfall totals are below average for this three-month period across most Western Australian cropping regions, and slightly above average for cropping regions of New South Wales. Above average soil moisture levels in Western Australia, and the probability of average or better in-season rainfall in September and October, will assist with maintaining or improving current yield potential in most winter cropping regions.
Rainfall totals that have a 75% chance of occurring September to November 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 05/08/2021
The temperature outlook for September to November 2021 indicates that maximum temperatures across most of Australia are likely to be close to the 1990-2012 average (- 1°C to 1°C). Minimum temperatures are expected to be slightly above average for much of Northern Australia (Bureau of Meteorology ‘National Climate Outlook’, 5 August 2021).
Predicted maximum temperature anomaly for September to November 2021
Predicted minimum temperature anomaly for September to November 2021
Rainfall forecast for the next eight days
The influence of slow-moving high-pressure systems is likely to bring clear skies and dry conditions across much of Australia over the next eight days. Rainfall is likely to be limited to west facing southern coastlines and onshore flow will bring showers to isolated areas of Australia’s eastern coast.
Rainfall totals of between 5 and 15 millimetres are forecast for isolated parts of southern and north-eastern New South Wales, north-eastern Queensland, as well as parts of Victoria, the south-east of South Australia, south-west Western Australia and Tasmania. Larger falls of between 15 and 100 millimetres are forecast for western Tasmania and parts of north-eastern Queensland.
Little to no rainfall is forecast for most of Australia’s cropping regions during the next 8-days.These dry conditions across most cropping regions will allow for drying of saturated soil profiles in some areas, reducing the impact of waterlogging and associated water-damage. Crop development is expected to progress unimpeded with high levels of plant available moisture provided by previous heavy falls. With the continuation of dry conditions from last week, growers will be able to gain unimpeded access to paddocks for top-dressing of fertilizer and for the allocation of pest and disease control programs in the coming week.
Total forecast rainfall (mm) for the period 12 August to 19 August 2021
©Commonwealth of Australia 2021, Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Issued: 12/08/2021
Water
Water storages, water markets and water allocations - current week
The Tableau dashboard may not meet accessibility requirements. For information about the contents of these dashboards contact ABARES.
Commodities
Information on weekly price changes in agricultural commodities is now available at the Weekly commodity price update.