Key issues
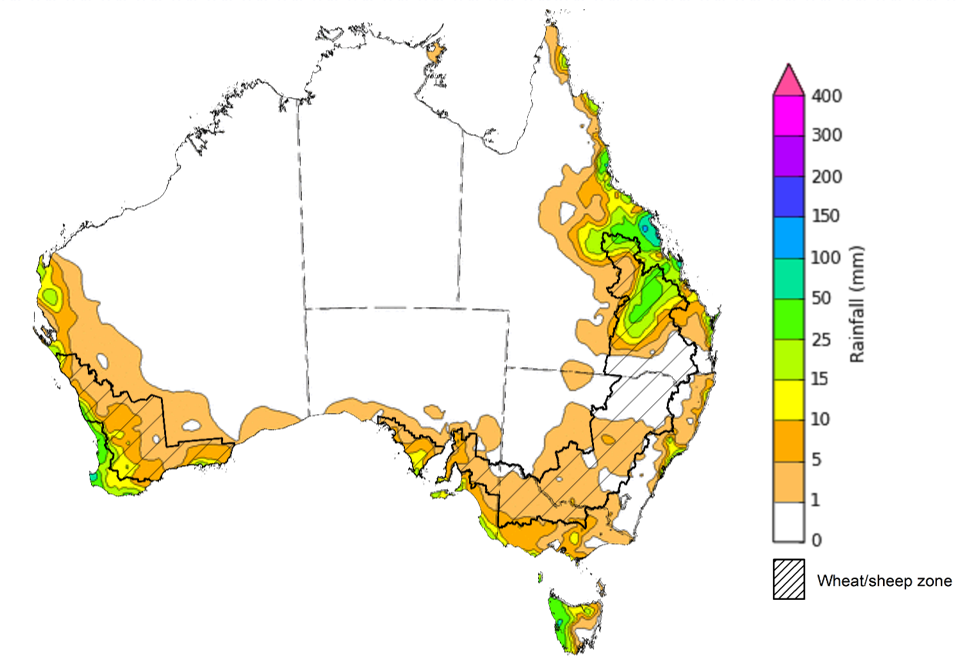
- For the week ending 26 July 2023, fronts brought some rainfall to southern Australia. A coastal trough brought rainfall to eastern Queensland. A high-pressure system kept the remainder of the country dry and clear.
- Across cropping regions, rainfall totals of up to 50 millimetres were recorded in central-north Queensland. These falls have likely benefited crop and pasture growth and built-up soil moisture reserves following widespread rainfall in early July. Elsewhere across Australia, falls of between 5 to 15 millimetres were recorded. This has likely only been enough to sustain crop and pasture growth but insufficient to build up soil moisture reserves. For remaining cropping regions, particularly in New South Wales, sufficient and timely rain will be required in the coming weeks and months to support at least average levels of winter crop production, following a gradual decline in soil moisture reserves (see Section 1.1).
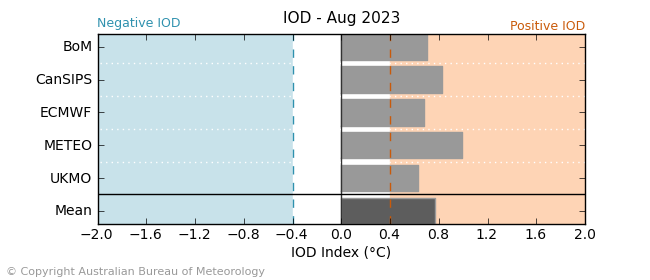
- The Bureau of Meteorology’s ENSO outlook remains at El Niño ALERT. Sea-surface temperatures in the Pacific have reached the El Niño thresholds but atmospheric indicators have returned to neutral range. There is also a strong possibility of a positive IOD event developing in late winter or early spring. A positive IOD can suppress winter and spring rainfall over much of Australia, potentially exacerbating the drying effect of El Niño (see Section 1.2).
- Drier than median conditions are expected in August to October for large areas of Australia. Across cropping regions, during August there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals of between 10 and 50 millimetres across southern and eastern New South Wales, and much of Victoria, South Australia and Western Australia. August rainfall totals are expected to be below 10 millimetres in the remaining cropping regions. During August to October 2023, below median rainfall is likely across cropping regions. There is 75% chance of receiving between 25 and 100 millimetres across most winter cropping regions, except for in Queensland where falls are expected to be below 25 millimetres. These falls are likely to be sufficient to support close to average plant growth. However, in areas with low soil moisture, such as Queensland and northern New South Wales these probable low three-month rainfall totals are unlikely to be sufficient to sustain average levels of crop and pasture production. Particularly as we enter the early months of spring, with higher temperatures and increased water demand for crops and pastures (see Section 1.3).
- Over the 8 days to 3 August 2023, a cold front is expected to bring showers to southern parts of the country early in the week. Onshore winds are expected to bring showers to coastal Queensland (see Section 1.4).
- Across cropping regions, rainfall totals of between 10 and 25 millimetres are expected in Western Australia, while falls of between 5 and 15 millimetres are expected in southern Victoria and isolated areas of New South Wales. If these falls eventuate as forecast, they are likely to be sufficient to support crop and pasture growth and development (see Section 1.4).
- Water storage levels in the Murray-Darling Basin (MDB) decreased between 20 July 2023 and 27 July 2023 by 3830 gigalitres (GL). Current volume of water held in storage is 17 032 GL. This is 17 percent or 3495 GL less than at the same time last year.
- Allocation prices in the Victorian Murray below the Barmah Choke increased from $100 on 20 July 2023 to $118 on 27 July 2023. Prices are lower in the Goulburn-Broken and regions above the Barmah choke due to the binding of the Goulburn intervalley trade limit and Barmah choke trade constraint.
Climate
For the week ending 26 July 2023, fronts brought some rainfall to southern Australia. A coastal trough brought rainfall to eastern Queensland. A high-pressure system kept the remainder of the country dry and clear.
Across cropping regions, rainfall totals of up to 50 millimetres were recorded in central-north Queensland. These falls have likely benefited crop and pasture growth and built-up soil moisture reserves following widespread rainfall in early July. Elsewhere, falls of between 5 to 15 millimetres were recorded. This has likely only been enough to sustain crop and pasture growth but insufficient to build up soil moisture reserves.
For remaining cropping regions, the clear dry conditions would have allowed for unimpeded field access to undertake pest and weed management and fertilizer top dressing of crops and pasture. These regions, particularly in New South Wales will require sufficient and timely rain in the coming weeks and months to support at least average levels of winter crop production, following a gradual decline in soil moisture reserves.
Rainfall for the week ending 26 July 2023
Note: The rainfall analyses and associated maps utilise data contained in the Bureau of Meteorology climate database, the Australian Data Archive for Meteorology (ADAM). The analyses are initially produced automatically from real-time data with limited quality control. They are intended to provide a general overview of rainfall across Australia as quickly as possible after the observations are received. For further information go to http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/rainfall/
The climate drivers with the largest potential impact on Australia’s climate patterns are the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and Southern Annular Mode (SAM). These climate drivers are likely to influence pasture growth across southern Australia and the growth and yield prospects for winter crops.
The Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO) pulse is currently over the western Pacific. This may contribute to El Niño development. At this time of the year MJO has little influence on northern Australia rainfall.
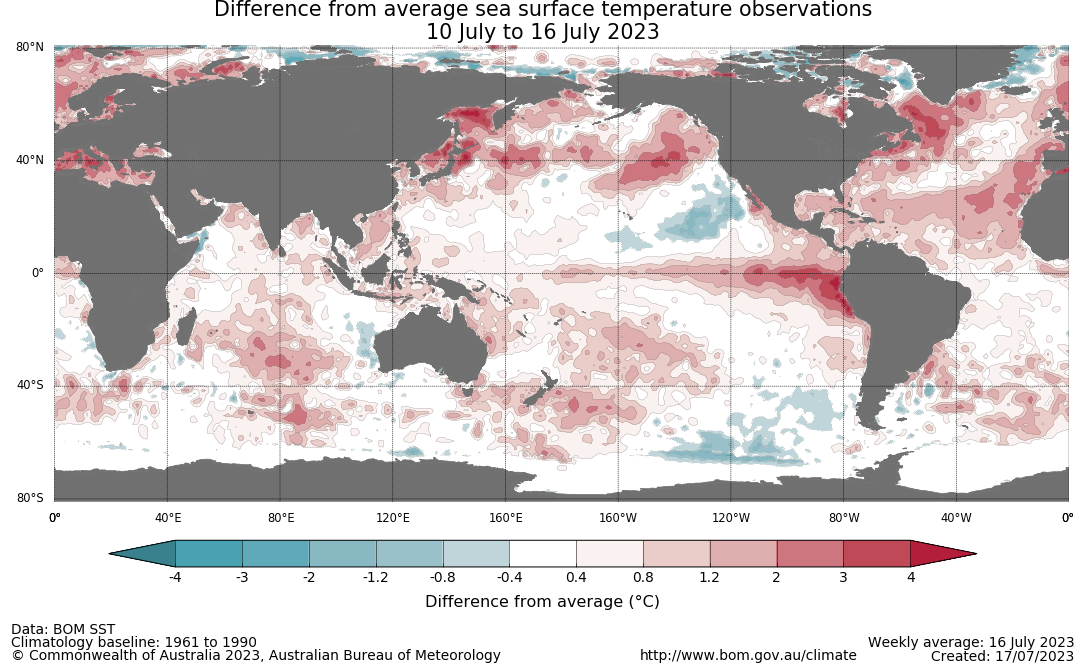
The Bureau of Meteorology’s ENSO outlook remains at El Niño ALERT, indicating that there is a 70% chance of El Niño developing in 2023. Oceanic indicators are measured in terms of the sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies, which have warmed to El Niño thresholds. For the week ending 16 July, SST anomalies were warmer than average over the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean, with anomalies over 4°C in the far east. SST anomalies have also been over 4°C off the Queensland coastline. Typically, during El Niño events, waters off of eastern Australia are cooler than average, pushing moisture flow from this region away from Australia. All models surveyed by the Bureau of Meteorology indicate the likelihood of further warming and the warm SSTs will remain above El Niño thresholds until at least end of the year.
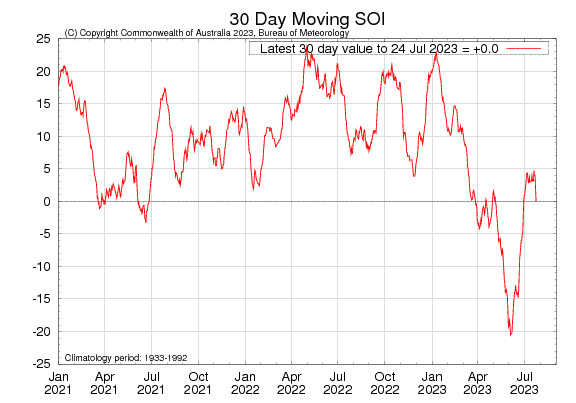
Atmospheric indicators are measured in terms of the surface air pressure difference between Tahiti and Darwin, called the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI), the direction and strength of the trade winds and cloudiness at the date line. Some atmospheric indicators such as the SOI have returned to neutral range. For the period ending 16 July 2023, the 30-day SOI was +3.9, the 60-day SOI was -4.8, and the 90-day SOI was -5.2. The 30-day values have remained fairly steady over the past 3 weeks. Additionally, winds, clouds and broadscale pressure patterns indicate that the ocean and atmosphere are yet to reinforce each other, as occurs during El Niño events. This is primarily due to the SSTs being warm globally. For Bureau of Meteorology to declare an El Niño, the contrast in SST between eastern and western Pacific has to be significant in order to drive the changes in wind patterns and surface pressure.
Difference from average sea surface temperature observations 10 July to 16 July 2023
30-day Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) values ending 24 July 2023
All international climate model surveyed by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology indicate the SST anomaly values will remain above El Niño threshold levels through spring and at least to the end of 2023. Note: the World Meteorological Organisation and other international agencies have declared that an El Niño event has already become established.
International climate model outlooks for the ENSO in NINO 3.4 region
Issued: 18/7/2023
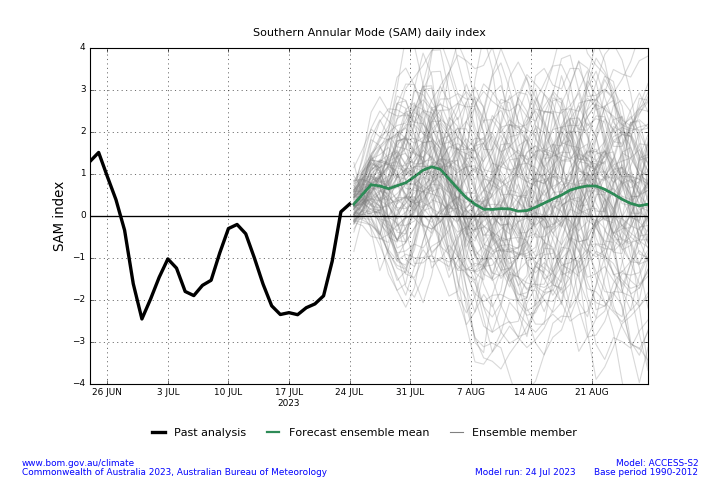
The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) index is currently neutral and is expected to remain at neutral levels for next few weeks. A neutral SAM has little influence on Australian climate.
Southern Annular Mode (SAM) daily index
These climate outlooks are generated by ACCESS–S (Australian Community Climate Earth-System Simulator–Seasonal). ACCESS–S is the Bureau of Meteorology's dynamic (physics-based) weather and climate model used for monthly, seasonal, and longer-lead climate outlooks. For further information, go to http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/ahead/about/.
The Bureau of Meteorology’s latest rainfall outlook for August 2023 indicates drier than average conditions are expected across large areas of central and southern Australia.
The ACCESS-S climate model suggests that there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 10 and 50 millimetres across eastern New South Wales, scattered areas of coastal Queensland, much of Victoria and Tasmania, southern South Australia, and southwest Western Australia. Rainfall totals in excess of 100 millimetres are expected across western Tasmania, far southwest Western Australia and alpine areas of Victoria.
Across cropping regions, there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals of between 10 and 50 millimetres across southern and eastern New South Wales, and much of Victoria, South Australia and Western Australia. August rainfall totals are expected to be below 10 millimetres in the remaining cropping regions.
Rainfall totals that have a 75% chance of occurring in August 2023
Issued: 27/07/2023
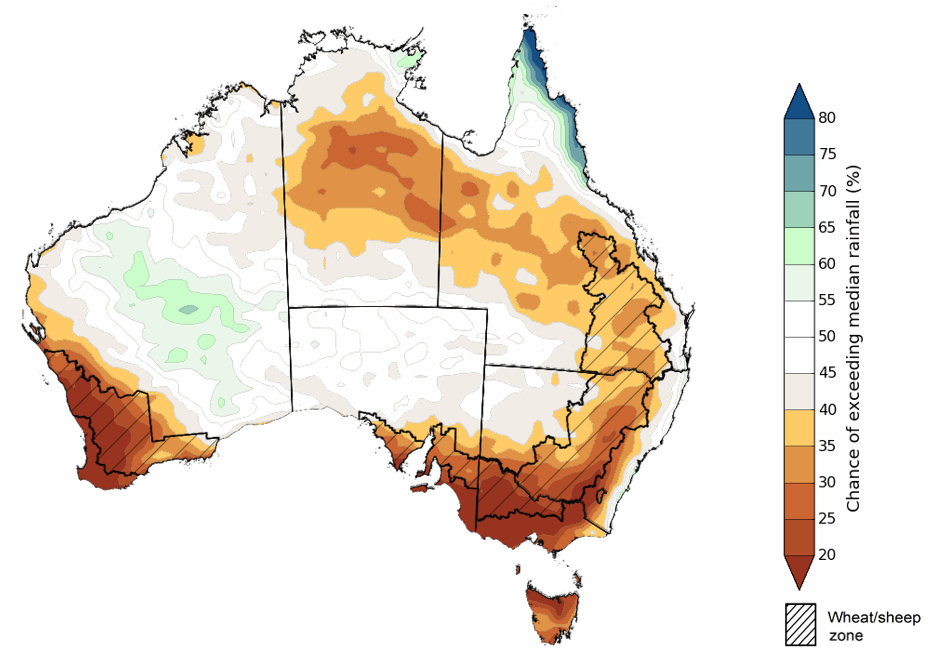
The rainfall outlook for August to October 2023 suggests that above median rainfall is likely to very likely (60% to greater than 80% chance) across large areas in central Western Australia and coastal tropical Queensland. There is close to equal chances of above or below median rainfall for parts of northern Western Australia, across much of South Australia, northwest New South Wales, and northern and southern parts of Northern Territory and Queensland. However, below average rainfall is more likely in across large areas of central Northern Territory to eastern Queensland and in large areas of New South Wales, southern South Australia, southwest Western Australia and across Victoria and Tasmania.
Across cropping regions, below median rainfall is more likely through the August to October period.
Chance of exceeding the median rainfall August to October 2023
Issued: 27/07/2023
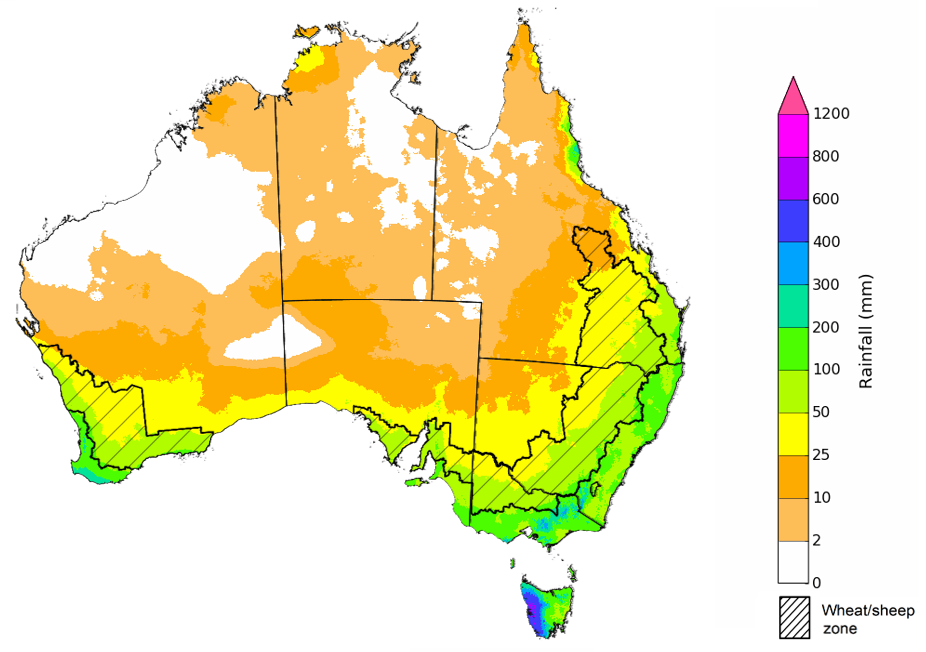
The outlook for August to October 2023 suggests there is a 75% chance of rainfall totals between 25 and 100 millimetres across much of New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania, parts of south-eastern and coastal Queensland, and southern parts of South Australia and Western Australia. Rainfall totals in excess of 200 millimetres are forecast for alpine regions of Victoria and New South Wales, the far southwest of Western Australia and western Tasmania.
There is a 75% chance of receiving between 25 and 100 millimetres across most winter cropping regions, except for northern cropping regions in Queensland where falls are expected to be below 25 millimetres. These falls are likely to be sufficient to support close to average plant growth. However, in areas with low soil moisture, such as southern Queensland, north-western New South Wales and northern and eastern Western Australia these probable low three-month rainfall totals are unlikely to be sufficient to sustain average levels of crop and pasture production. Particularly as we enter the early months of spring, with higher temperatures and increased water demand for crops and pastures.
Rainfall totals that have a 75% chance of occurring August to October 2023
Issued: 27/07/2023
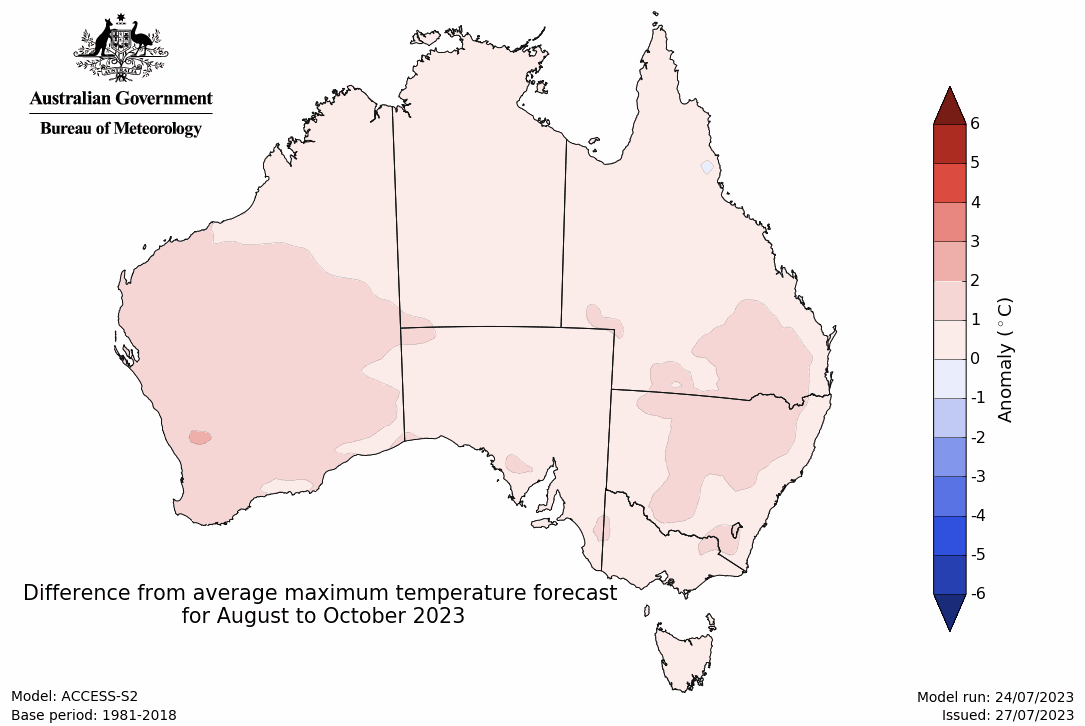
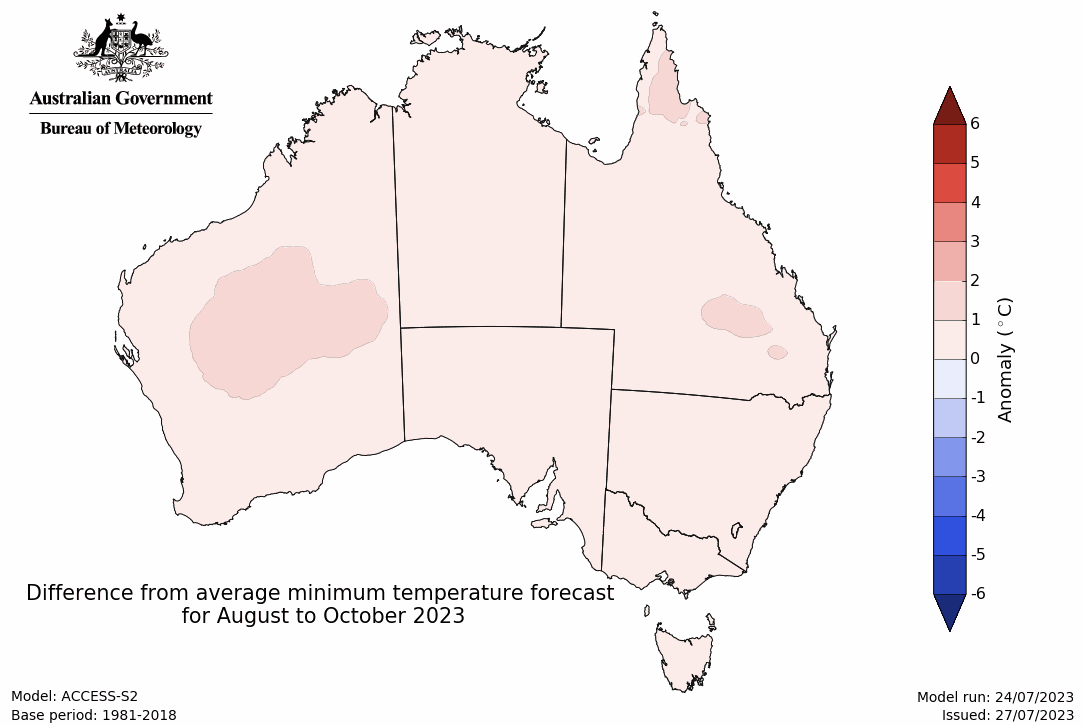
The temperature outlook for August to October 2023 indicates that maximum temperatures across northern Australia, most of South Australia, the east coast, Victoria and Tasmania are likely to be close to the 1990–2012 average (-1°C to +1°C). Meanwhile maximum temperatures are expected to be warmer than average (above +1°C) across much of the remainder of southern Australia. Minimum temperatures are expected to be close to the 1990–2012 average (-1°C to +1°C) across most of Australia. The night-time temperatures in central parts of Western Australia are likely to be warmer that average (above +1°C).
Predicted maximum temperature anomaly for August to October 2023
Predicted minimum temperature anomaly for August to October 2023
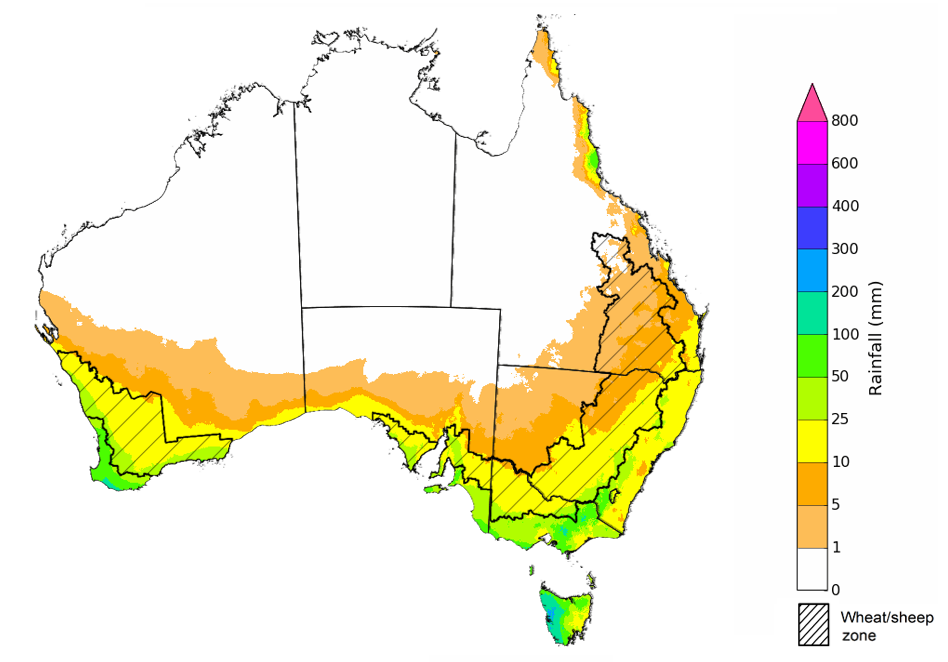
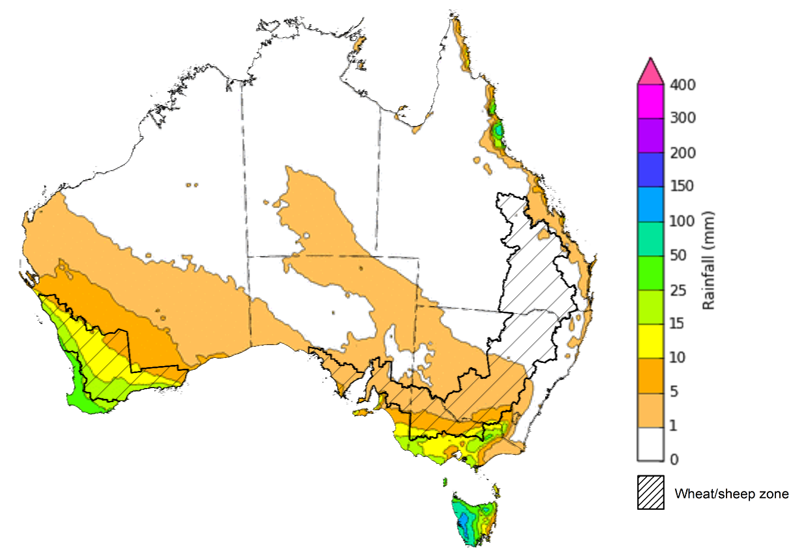
Over the 8-days to 3 August 2023, a cold front is expected to bring showers to southern parts of the country early in the week. Onshore winds are expected to bring showers to coastal Queensland. A high-pressure system is expected to bring mainly dry conditions to the remainder of the country.
Across cropping regions, rainfall totals of between 10 and 25 millimetres are expected in Western Australia, while falls of between 5 and 15 millimetres are expected in southern Victoria and isolated areas of New South Wales. If these falls eventuate as forecast, they are likely to be sufficient to support crop and pasture growth and development.
Total forecast rainfall for the period 27 July 2023 to 3 August 2023
Note: This rainfall forecast is produced from computer models. As the model outputs are not altered by weather forecasters, it is important to check local forecasts and warnings issued by the Bureau of Meteorology.
Water
Water storages, water markets and water allocations - current week
The Tableau dashboard may not meet accessibility requirements. For information about the contents of these dashboards contact ABARES.
Commodities
Information on weekly price changes in agricultural commodities is now available at the Weekly commodity price update.